

Here’s a brief overview of each: Comparative advantageĬomparative advantage occurs when one country or other organizational units can produce a material more efficiently than another. Types of advantages in the production possibility curveĬountries and other organizational units can experience two main types of advantage in the context of PPC: comparative advantage and absolute advantage. This tool is likely to be more relevant for people or groups who produce quantifiable goods. They, probably use it less frequently than economists and business leaders. Individuals and families who want to understand the relationship between their economic resources and their own productivity might use the PPC. Related: Opportunity Cost: Definition and Example Individuals
#PRODUCTION POSSIBILITIES CURVE HOW TO#
It might also help make decisions regarding the types of materials to use and how to source them. This could help them make informed decisions regarding which items to produce, how many to create and what kinds of materials to use. Related: Understanding Economics: Definition and Application Business leadersīusiness leaders might evaluate their production levels and available resources using the PPC. Examples of policy recommendations include wage adjustments and price stability. They could use their understanding of the balance between resources available and production possibility to make informed policy recommendations. Here's how three main demographics might use this tool to their advantage: Macro- and micro-economistsĮconomists and analysts might use the production possibility curve to understand and predict the production potential in a country, state, city or other social or geographic unit. Who uses the production possibility curve?ĭifferent professionals use the PPC in different ways. This might motivate the strategic decisions of the businesses that grow and process these foods. For example, if one state grows plentiful pears and another grows abundant asparagus due to the natural conditions of the land, each state might develop trade agreements to help them focus on their most successful product.
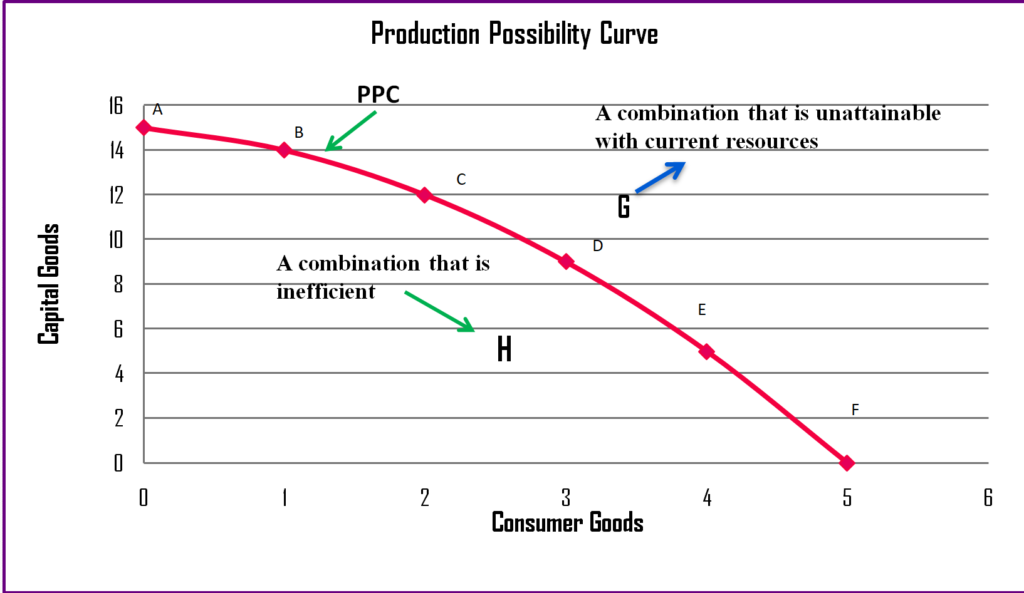
This may also be true at a microeconomic or business level if an organization uses this information to understand how much of a particular product they can create.Īt both a broad and specific level, the PPC can help analysts understand the tradeoffs involved in the production of specific items and then use that information to make informed decisions. Countries might also use this information to determine what and how much of a particular item to trade, given the relative efficiency of their own production processes. On a macroeconomic level, this can help economists understand and project a country or other unit's productive activity. The production possibility curve is important because it can help demonstrate the maximum possible output of goods given a set amount of resources.
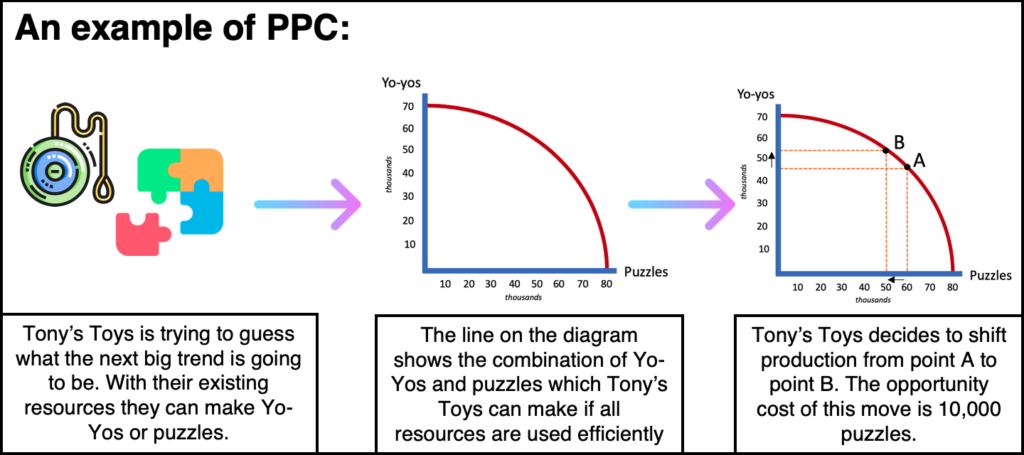
Related: Guide to Supply Schedules Importance of the production possibility curve Professionals most frequently represent it as a curve across two axes representing the two materials they’re comparing. This calculation is common in economics and you can also apply it to matters of personal or home finance and business purposes. The relationship between a fixed input quantity and the two goods may sometimes be called the production possibility frontier (PPF). In fact, most developed products require a combination of all of these elements, though they might require fewer.

The input in this calculation can include natural resources, labor, capital and entrepreneur activity. The product, or production, possibility curve is a way to calculate the highest possible output of two goods using a fixed input quantity. In this article, we explain the production possibility curve (PPC), its importance and advantages and some examples to help you reach your own career goals. This graphic representation demonstrates the relationship between the resources you use in production and how many of an item you can produce. The product possibility curve concept, for example, can help you understand a group's productivity potential and make decisions accordingly. Economic principles can help guide the decisions of countries, businesses and individuals, depending on how you apply them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
